How DNS Works
Understanding DNS
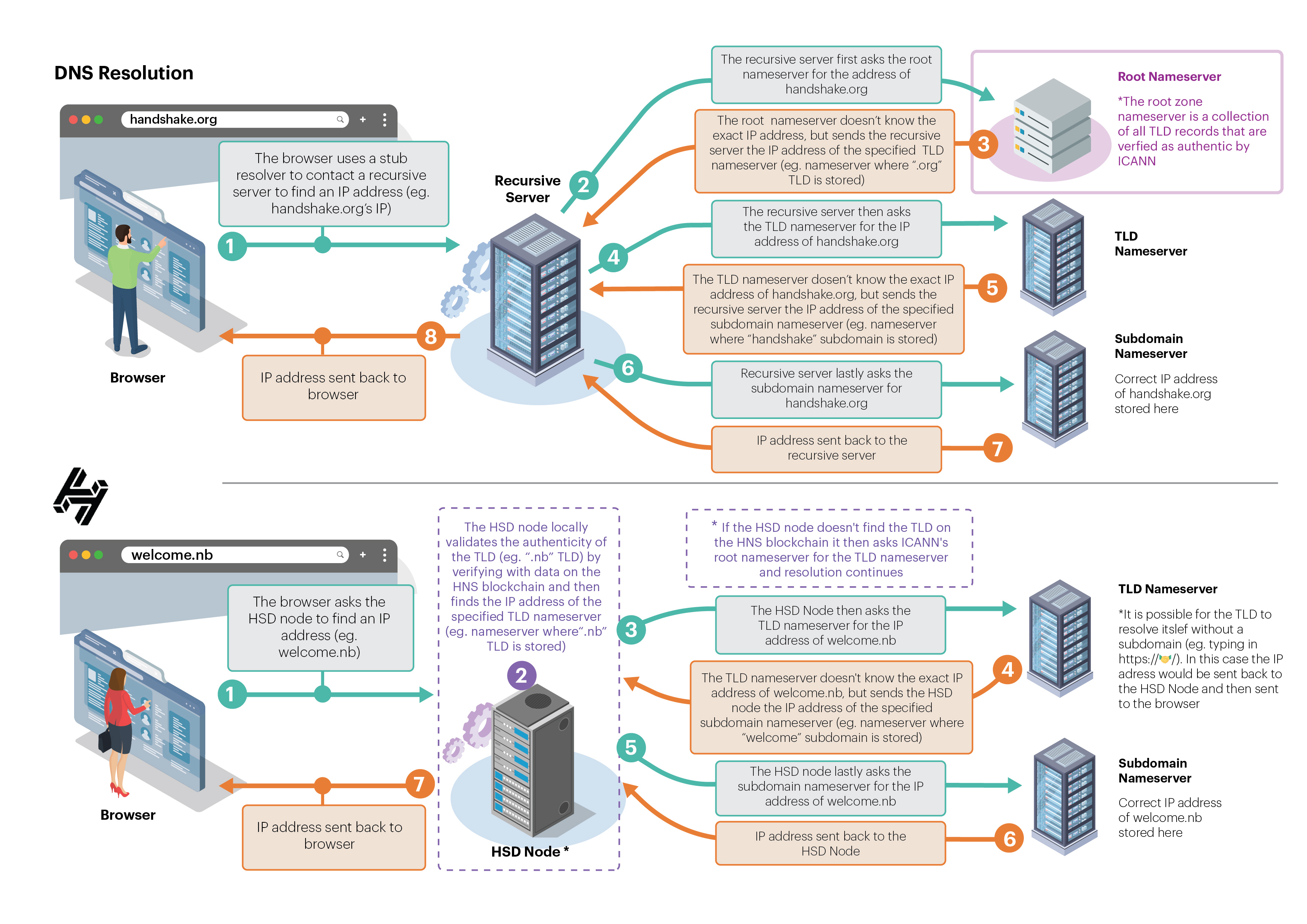
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the internet's address book, translating human-readable domain names into IP addresses.
Key Differences: Traditional DNS vs Handshake
-
Centralization vs Decentralization
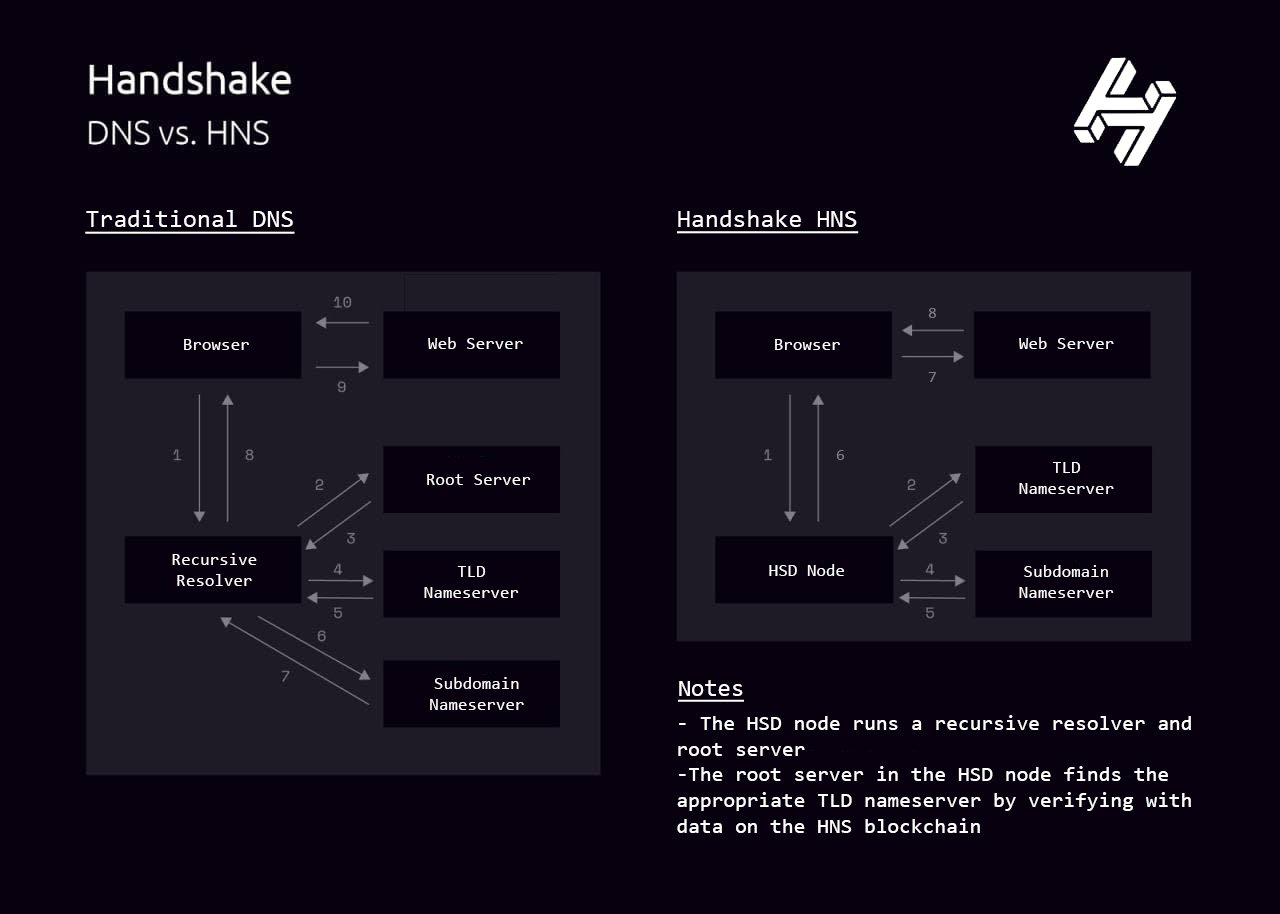
Traditional DNS relies on centralized authorities (ICANN, registrars) while Handshake creates a decentralized root zone managed by blockchain consensus.
-
Security Model
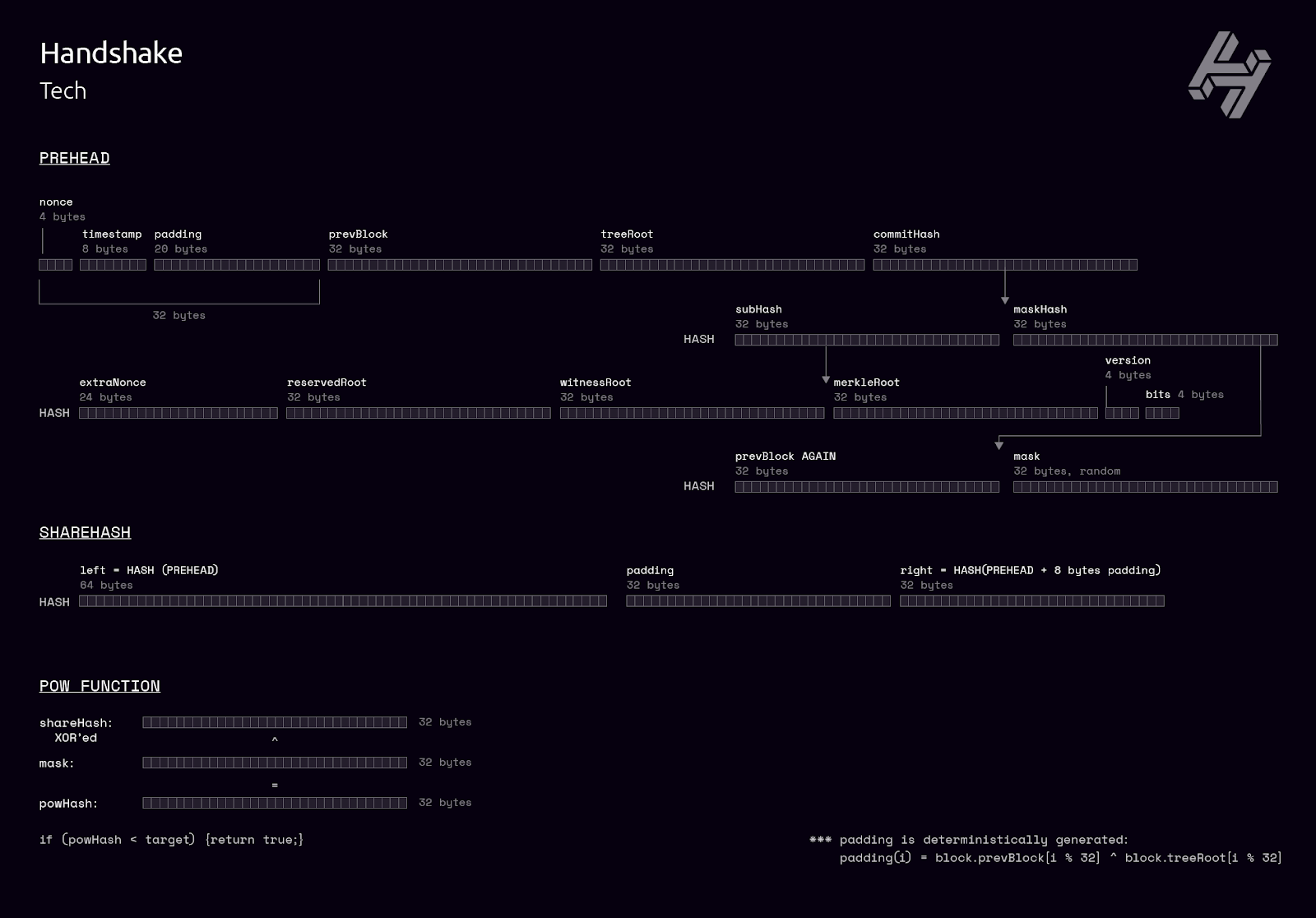
DNS uses DNSSEC for security, while Handshake leverages blockchain technology and cryptographic proofs for enhanced security.
-
Name Ownership
Traditional domains are rented through registrars, while Handshake names are truly owned through blockchain-based assets.
Essential Resources
-
Public Resolvers
Configure your system to resolve Handshake names
-
Technical Deep Dives
Understanding the technical aspects of Handshake DNS
-
Educational Articles
Learn more about DNS and Handshake